2021 Advanced Course Test Questions with Answers:
2021 Advanced Exam Certification 94% Pass ProofAdvanced Scenario 1: Test Questions Karen White;
1. What is the most beneficial filing status that Karen is eligible to claim on her 2021 tax return?a. Single
b. Married Filing Separately
c. Married Filing Jointly
d. Head of Household
Question 1 — Explanation:
Can Married Filing Separately taxpayers qualify for another status?
Some married taxpayers may be considered unmarried even if they are not divorced or legally separated. Such taxpayers may be able to use the Head of Household filing status, which may result in a lower tax than Married Filing Separately.
2. Karen’s Economic Impact Payment (EIP3) must be included in her total income.
a. True b. False
No, the EIP3 payment is not includible in your gross income. Therefore, you will not include the payment in your taxable income on your federal income tax return or pay income tax on your payment. It will not reduce your refund or increase the amount you owe when you file your 2021 federal income tax return.
3. What amount may Karen deduct as a charitable contribution when filing her 2021 tax return?
a. $650 b. $600 c. $300 d.$0
Question 3 — Explanation: Charitable contribution deduction for individuals who don't itemize.
A charitable contribution is a donation or gift to a qualified organization. Charitable contributions new expanded tax benefit is to help individual 2021 tax filers, who does not itemize, including married individuals filing separate returns, can now (2021) claim a deduction of up to $300 for cash contributions made to qualifying charities during 2021. The maximum deduction is increased to $600 for married individuals filing joint returns.
Karen made a cash contribution of $650 to the Red Cross. She does not have to itemize for year 2021 and can claim a deduction of up to $300.
Form 1040 Line 12b Charitable contributions if you take the standard deduction and don’t itemize:
If you don't itemize deductions on Schedule A (Form 1040), you (or you and your spouse if filing jointly) may be able to take a charitable deduction for cash contributions made in 2021. Enter the total amount of your contributions on line 12b. Don't enter more than $300 ($600 if married filing jointly).
Retest Question 3. Karen’s deductible charitable contribution for 2021 does not reduce her adjusted gross income (AGI). The correct answer is True.
Small Capital Options Trader Rules Money Control and Power Your Trade:
Options are very different from Stock and therefore Options rules are very different as Options have a very small shelf life mostly a month comparted to Stocks.- Position Sizing
- Setting the Holding Period
- Pre-calculate Stops and Targets
- Limit number of open trades 10 Contracts 3 and 3 and 4
- Range Bound Trading
- Mid-Morning Revesal
- Late-Day Snapback
- Afternoon Snapback
- Options EveryDay Profits
Trade Morning Reversals and You'll be making Money just by watching the Clock. Every Day is Different, but watch the Clock for:
- -Middle of the Morning Reversals
- -Early Afternoon, Pullbacks or Breakouts
- -End of Day Snapbacks
Gauge the Strength of the various Markets and know what it means to your Options trading:
- -80% of the Time Markets move together
- -Sometimes one index is stronger than the other
- -If that index is leading, you can see where the other Markets will follow.
- -An easy going Market
- -See-Saw kind of day Market
- -Or is it a Raging Breakout Trend Market
- -Find Every Day Profits with Intraday Trading
- Options as a Strategic Investment: Fifth Edition Hardcover — 2012 by Lawrence McMillan.
“Options as a Strategic Investment,” provides traders with practical option trading strategies designed to minimize risk and maximize profit potential. Inside this revised edition are scores of proven business-tested tactics for investing and the techniques for using index options and futures to protect one’s portfolio and improve one’s return; and the implications of the tax laws for option writers, including allowable long-term gains and losses.
- Options as a Strategic Investment Fifth Edition STUDY GUIDE by Lawrence G. McMillam — Paperback Illustrated 2012.
Author Lawrence G. McMillan is a professional trader and the author of the bestselling Options as a Strategic Investment. He is recipient of Sullivan Award for his contribution to the growth and integrity of the US options markets. He is founder and president of McMillan Analysis Corporation. This Study Guide for the Fifth Edition will help you maximize your understanding of options, thereby increasing your profits.
- Option Volatility and Pricing: SECOND Edition Hard Cover — 2014 by by Sheldon Natenberg.
The bestselling “Option Volatility and Pricing” has made Sheldon Natenberg a widely recognized authority in the option industry. Option trading is both a science and an art and this book shows how to apply both to maximum effect. You'll learn how professional option traders approach the market, including the trading strategies and risk management techniques necessary for success.
- Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets Pearson 9th Edition 2016 by John Hull Hardcover 624 pages Look inside Buy new: $207.98 In Stock ISBN 978-0134083247.
Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets, simplifies the language for a less mathematically sophisticated audience. The Ninth Edition of Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets offers easy-to-grasp introduction into financial mathematics. John Hull is the Maple Financial Professor of Derivatives and Risk Management at the Joseph L. Rotman School of Management, University of Toronto. He is an internationally recognized authority on derivatives and risk management with many publications in this area.
- Trading Options Greeks: How Time, Volatility, and Other Pricing Factors Drive Profits Second Edition by Dan Passarelli —Bloomberg Press 2nd edition Hardcover Illustrated 2012 368 pages ISBN 978-1118133163 In Stock Buy new: $52.50.
In the Second Edition of Trading Options Greeks, options trader Dan Pasarelli is offering fresh insights on option trading and valuation. He makes use of new charts and examples, and discusses how the proper application of the greeks can lead to more accurate pricing and trading. Dan Passarelli, is the author of the book Trading Option Greeks and founder of Market Taker Mentoring LLC an options education company that provides personalized one-on-one mentoring for option traders.
- The Option Trader's Hedge Fund: A Business Framework for Trading Equity and Index Options Paperback 1st Edition by Dennis Chen (Author), Mark Sebastian (Author) FT Press 2017; Paperback: 240 pages, ISBN-13: 978-0134807522, In Stock Buy new $43.49.
This book will show you how to master the five essential components of high-profit option trades and manage all your risks--including black swan risks. Dennis A. Chen is a hedge fund manager. He is the founder and Chief Investment Officer of Smart Income Partners, Ltd., a hedge fund specializing in generating income using index and equity options. Author Dennis A. Chen earned his MBA from The Wharton School of Business. He also holds a Master’s in Computer Science from Arizona State University and a Bachelor’s degree in computer science from the University of Texas. Author Mark Sebastian has a Bachelor’s of Science in finance from Villanova University of Pennsylvania. Mark Sebastian is the Founder of OptionPit.com.
- Options Trading Crash Course: The #1 Beginner's Guide to Make Money with Trading Options in 7 Days or Less! Paperback 112 pages Publisher eBookIt.com 2020 ISBN 978-1456636104 In Stock Buy new $9.95 Reviews 4.2, 239 Ratings.
Author Frank Richmond is an economist by trade. Frank found the options market too strong to ignore to make a successful investment. Everything Frank knows he learned through years of experience. Frank’s book “Options Trading Crash Course” is in a perfect position to help newcomers to learn options in an intuitive and easily understandable way.
- Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives 10th Edition Pearson 2017 by John Hull (Author) Hardcover 896 pages ISBN-13 978-0134472089 Buy new $261.32 College Graduate and Undergraduate levels.
- Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives 9th Edition by John C. Hull (Author) 4.5-146 Ratings Buy use $227.34 Hardcover 896 pages ISBN 978-0133456318 PDF for Free Download.
Options Futures and Other Derivatives 9th Edition by Professor John C. Hull is designed for graduate courses in business, economics, financial mathematics, and financial engineering; for advanced undergraduate courses with students who have good quantitative skills; and for practitioners involved in derivatives markets. John C. Hull is a Professor of Derivatives and Risk Management at the Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto.
- Options Trading Crash Course 2 Books in 1: A Guide for Beginners to Build Passive Income. Make Profit in the Next 60 Days Working from Home by Richman Publications Paperback – 2021 275 Pgs. 979-8780531500
 Richman Publications is a company that brings together many of the most experienced American investors, founded in 2015 by five professional traders. Richman Publications hopes to reach all those people who are eager to take a step towards their financial freedom, to give them the knowledge to take that step in the most correct and profitable way possible.
Richman Publications is a company that brings together many of the most experienced American investors, founded in 2015 by five professional traders. Richman Publications hopes to reach all those people who are eager to take a step towards their financial freedom, to give them the knowledge to take that step in the most correct and profitable way possible.
- $25K Options Trading Challenge Second Edition: Proven techniques to grow $2,500 into $25,000 using Options Trading and Technical Analysis 2020 by Nishant Pant (Author) Paperback 161 Pgs. 979-8694166201 In Stock Buy new $24.99 4.4 star at 670 ratings Ships from Amazon.com Sold by Amazon.com
 In this book you will learn:
In this book you will learn:
1. NEW: Finding the right stocks for the $25K Options Challenge.
2. NEW: Money management techniques so you don't get wiped out in the next Stock Market correction.
3. NEW: Techniques to participate in earnings while avoiding the binary outcome of these events.
4. How to become a winner in the stock market by spotting the right trading opportunities.
5. A simple strategy that keeps doubling your money over and over again.
6. A strategy to overcome the premium buyer's greatest enemies, Theta and Implied Volatility.
7. How to use simple Technical Analysis techniques to spot the right entry points for your trades.
8. Live Trade examples elaborating all the concepts in this book.
9. Plus you can join us on our website to view our live trades on www.25koptionschallenge.com.
-
Options Made Easy: Your Guide to Profitable Trading 3rd Edition by Guy Cohen (Author) 4.1 stars at 98 ratings Buy new $29.18 In Stock Ships from and sold by Amazon.com. Save $29.18 plus tax, using our free download option.
 Options Made Easy is the Guide to Making Consistent Options Profits. The Third Edition is now Fully Updated with New Examples and Powerful New Strategies! The book teaches you all the essentials with real-life examples and clear explanations. No complicated math or confusing jargon. Learn visually with easy-to-understand pictures! Includes new ways to use chart patterns to identify high-probability trades and design winning trading plans. Master Guy Cohen’s unique OVI for anticipating stock moves in time to earn big profits!
Options Made Easy is the Guide to Making Consistent Options Profits. The Third Edition is now Fully Updated with New Examples and Powerful New Strategies! The book teaches you all the essentials with real-life examples and clear explanations. No complicated math or confusing jargon. Learn visually with easy-to-understand pictures! Includes new ways to use chart patterns to identify high-probability trades and design winning trading plans. Master Guy Cohen’s unique OVI for anticipating stock moves in time to earn big profits!
- OPTION TRADING STRATEGIES: HSBC InvestDirect Self-Directed Online Investing Services (Free Download).
- OPTIONS and FUTURES: A Tutorial by CFA Institute Roger G. Clarke (Free Download).
- If your filing status is single.
- AND at the end of 2021 you were under 65.
- THEN you must file a return if your gross income was at least $12,550.
- Demonstrate that their tax home is in a foreign country.
- Meet either the bona fide residence test or the physical presence test.
- Have income that qualifies as foreign earned income.
- Residency status,
- Use of Form 8843, and
- Filing status.
Know the Market's Mood:
Description of MoneyControl.com is the greatest resource for financial information on the Internet:
- moneycontrol.com is 2 decades 3 years old. moneycontrol.com has #674 ranking worldwide. - moneycontrol.com has 6/10 Google PageRank value.Description of Bloomberg.com:
About Bloomberg.com: Bloomberg is the global leader in business and financial data and news.Bloomberg connects the world’s decision makers to accurate information on the financial markets – and helps them to make faster and smarter decisions.
Bloomberg delivers business and markets news, data, analysis, and video to the world.
S&P 500 3941.48 -0.81%
Nasdaq 11264.45 -2.35%
Dow Jones 31928.62 +0.15%
Description of Investopedia.comm:
About: The mission of Investopedia.com is to simplify financial decisions and information to give readers the confidence to manage every aspect of their financial life. Our millions of readers come to us from all over the world and from all walks of life. Some are learning about money and investing for the first time, while others are experienced investors, business owners, professionals, financial advisors, and executives looking to improve their knowledge and skills. No matter who they are, we are here to help. Investopedia is a part of the Dotdash Meredith publishing family.TD Ameritrade thinkorswim for trading Options:
Options involve risks and are not suitable for all investors. Before trading, read the Options Disclosure Document: https://bit.ly/2v9tH6D.thinkorswim® is one of the most powerful options trading platforms around, but if you’re just sticking with the default settings, you’re missing out. Watch this video 'How to Set Up thinkorswim® for Trading Options' for some insider tips on how to customize the platform especially for options, things like streamlining the Option Chain based on your trading style, setting up custom options screeners, and more features you don’t want to miss.
Explore Oil and Gas Investment Opportunity:
 There has never been a better time to invest in Oil and Gas. Above average returns, long term residual income an 100% tax write offs. Explore investment opportunities at invest.hornetcorp.com. If you are a savvy Accredited Investor, looking to expand your portfolio reach out to us today.
There has never been a better time to invest in Oil and Gas. Above average returns, long term residual income an 100% tax write offs. Explore investment opportunities at invest.hornetcorp.com. If you are a savvy Accredited Investor, looking to expand your portfolio reach out to us today.WHY CHOOSE HORNET CORP THE ROCK SOLID COMPANY?
1. Hornet Drills Shallow Inexpensive Wells. No Expensive Horizontal Drilling or Fracking.
2. Hornet Has Very Low Operating Costs.
3. A Hornet Well Doing 20 Barrels of Oil Per Day (BOPD) @ $35 Oil Will Pay Off in Less Than 2 Years! At $50 Oil That Well Will Pay Off in 13 Months!!!
*And That Does Not Include the Tax Savings!
4. Hornet’s Average Time from Investment to Completed Drilling is 60-120 days!
5. Hornet Employs an "Environmentally Sound" Drilling Strategy.
*The information above is for example only. Actual results may differ. Oil and Gas Exploration is a speculative endeavor.
HOW IT WORKS Three simple steps to get you started:
1. Investor purchases ownership in a partnership that will drill multiple oil wells.
2. Investor receives a percentage of the revenues from producing wells in the partnership directly correlating to the amount of their ownership.
3. Investor can deduct approximately 85% of the Investment from their Ordinary Income or Capital Gains in the Year the Investment was made. The remaining 15% is deducted over 5 years.
Books To Become an Options Trader:
Advanced Scenario 2: Test Questions Paul and Maggie Thomas.
4. What is the maximum amount Paul and Maggie are eligible to claim for the child tax credit?a. $3,000 b. $3,600 c. $6,000 d. $6,600
The new law for 2021 is $3,000 per qualifying child ages 6 through 17, and $3,600 for qualifying children ages 5 and under. For eligible taxpayers the credit is fully refundable for 2021. Previously, the refundable portion was limited to $1,400 per child.
5. How much of the child care expenses can be used to claim the child and dependent care credit?
a. $3,500 b. $3,000 c. $1,500 d. $0
IRS Child and Dependent Care Credit Information:
The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021, was enacted on March 11, 2021, making the Child and Dependent Care credit substantially more generous and potentially refundable (up to $4,000 for one qualifying person and $8,000 for two or more qualifying persons) only for the tax year 2021, This means an eligible taxpayer can receive this credit even if they owe no federal income tax. Your federal income tax may be reduced by claiming the Credit for Child and Dependent Care expenses on your tax return.
Paul and Maggie are married and want to file a joint return. Maggie is a U.S. citizen and has a valid Social Security number. Paul is a resident alien and has an ITIN. Can Paul and Maggie claim Child Tax Credit for their two children?
Note: If you don’t have a ITIN by the due date of your return, you may not claim the CTC/ACTC on either your return. However, if you apply for an ITIN on or before the due date of your return and the IRS issues you an ITIN as a result of the application, the IRS will consider your ITIN as issued on or before the due date of your return.
What is the child and dependent care credit?
This credit allows taxpayers to reduce their tax by a portion of their child and dependent care expenses. The credit may be claimed by taxpayers who, in order to work or look for work, pay someone to take care of their qualifying person. A qualifying person is a Qualifying child under age 13.
Advanced Scenario 3: Test Questions Carol Wheeler
6. Form 8889, Part 1 is used to report HSA contributions made by _______________.a. Carol b. Carol’s employer
c. Carol’s cousin d. All the above
Contributions to HSA: For an employee’s HSA, the employee, employer, or both may contribute to the employee’s HSA in the same year. Family members or any other person may also contribute on behalf of an eligible individual. Contributions to an HSA must be made in cash.
IRS 2021 changes: Contributions, other than employer contributions, are deductible on the eligible individual’s return whether or not the individual itemizes deductions. For 2021, if you have self-only HDHP coverage, you can contribute up to $3,600. If you have family HDHP coverage, you can contribute up to $7,200.
7. Carol is eligible to contribute an additional $________ to her HSA because she is age 55 or older. 1000
Health Savings Account (HSA) Deduction:
For 2021, the annual contribution limits on deductions for HSAs for individuals with self-only coverage is $3,600 (increase of $50) and $7,200 for family coverage (increase of $100). There is an additional contribution amount of $1,000 for taxpayers who are age 55 or older.
8. What is the total unreimbursed qualified medical expense reported on Form 8889, Part II?
a. $2,600 b. $2,900 c. $2,980 d. $3,105
Over-the-counter products and medications are now reimbursable without a prescription from HSAs accounts that means that additional items are now “qualified medical expenses” that may be reimbursed from HSAs accounts. And that is because the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act modifies the rules that apply to tax-advantaged accounts like HSAs.
What is Form 8889, Part I used for?
Form 8889, Part 1, is used to report all HSA contributions and to compute the allowable HSA deduction. Contributions made by an employer are also shown in Part I, but are not included in the deductible amount. An HSA may receive contributions from any individual, including an employer or a family member.
What is Form 5498-SA?
The 5498-SA tax form is used to report contributions to a health savings account (HSA). It is for informational purposes and is not required to file a tax return. it shows the fair market value of your HSA account. Box 6 shows the type of account that is reported.
Advanced Scenario 4: Test Questions Barbara Jacobs
9. For the purpose of determining dependency, Marie meets the conditions to be the qualifying child of _______________.a. Barbara b. Jenny
c. Both Barbara and Jenny
d. Neither Barbara nor Jenny
Qualifying child to meet dependency condition:
To claim your child as your dependent, your child must meet either the qualifying child test or the qualifying relative test: To meet the qualifying child test, your child must be younger than you and either younger than 19 years old or be a "student" younger than 24 years old as of the end of the calendar year. There's no age limit if your child is "permanently and totally disabled" or meets the qualifying relative test.
10. Jenny is not eligible to claim Marie for the earned income credit because her filing status is Married Filing Separate.
a. True b. False
You can claim the EITC if your filing status is married filing separately. To figure the credit, see Publication 596, Earned Income Credit 2021. When you file Form 1040 or 1040-SR, you must attach Schedule EIC to your return to claim the EIC with a qualifying child.
What is earned income credit?
2021 — The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) helps low-to-moderate-income workers and families get a tax break.
Advanced Scenario 5: Test Questions Michael Block
11. Michael’s mortgage insurance premium of $230 can be claimed as an itemized deduction on his Schedule A.a. True b. False
Question 17 — Explanation: Taxpayers can deduct private mortgage insurance premiums paid during the current tax year on Schedule A in the Interest You Paid section.
12. What amount of gambling losses is Michael eligible to claim as a deduction on his Schedule A?
a. $0 b. $500 c. $1,000 d. $2,000
Gambling Winnings and Losses:
The taxpayer may receive one or more Forms W-2G reporting gambling winnings. Total gambling winnings must be reported as other income. If the taxpayer also had gambling losses, the losses can only be deducted on Schedule A. Gambling losses in excess of winnings are not deductible. And therefore the correct answer is $1,000, because the $1,000 was the amount of winning.
Advanced Scenario 6: Test Questions Sean Dennison
13. Sean is not required to file a tax return because he has enough tax withholding to cover his tax liability.a. True b. False
Who is legally required to file a federal tax return?
a. Sean must have a Social Security number valid for employment.
b. Sean must be at least age 25 but under age 65 on December 31.
c. Sean’s adjusted gross income must be below $21,430.
d. Sean cannot be the qualifying child of another taxpayer.
1. Must have a Social Security number valid for employment;
2. Adjusted gross income must be below $21,430.
3. Cannot be the qualifying child of another taxpayer;
What are the changes to EITC for 2021?
In the past, the EITC for those with no qualifying children was only available to people ages 25 to 64. In 2021 if you're not claiming a qualifying child, you must be at least 19 years old to qualify for Earned Income Credit (EIC).in 2021. The upper age limit is eliminated for 2021.
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) Relief for 2021.
If your earned income was higher in 2019 than in 2021, you can use the 2019 amount to figure your EITC for 2021.
Advanced Scenario 7: Gilbert and Tara Washington Interview Notes.
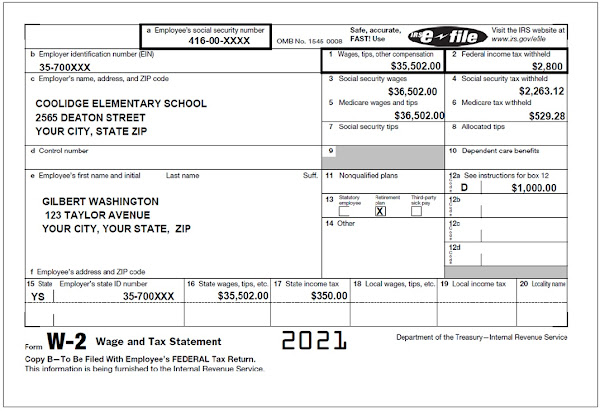
• Gilbert is an elementary school teacher at a public school. Gilbert and Tara are married and choose to file Married Filing Jointly on their 2021 tax return.• Gilbert worked a total of 1,280 hours in 2021. During the school year, he spent $500 on unreimbursed classroom expenses.
• Tara retired in 2018 and began receiving her pension on October 1st of that year. She explains that this is a joint and survivor annuity. She has already recovered $1,013 of the cost of the plan.
• Gilbert settled with his credit card company on an outstanding bill and brought the Form 1099-C to the site. They aren’t sure how it will impact their tax return for tax year 2021.The Washingtons determined that they were solvent as of the date of the canceled debt.
• Tara won $3,000 gambling at a casino and had additional lottery winnings of $150. Tara has documented casino losses of $1,500.
• Their son, Chandler, is in his second year of college pursuing a bachelor’s degree in Logistics at a qualified educational institution. He received a scholarship and the terms require that it be used to pay tuition. Box 2 was not filled in and Box 7 was not checked on his Form 1098-T for the previous tax year. The Washingtons provided Form 1098-T and an account statement from the college that included additional expenses. The Washingtons paid $450 for books required for Chandler’s courses. This information is also included on the College statement of account.
• Chandler does not have a felony drug conviction.
• The Washington’s did not receive the third Economic Impact Payment (EIP 3) in the amount of $4,200. The Washington’s want to claim the third Economic Impact Payment (EIP 3) in the amount of $4,200 on their 2021 tax return.
• They are all U.S. citizens with valid Social Security numbers.
Income and documents – Year 2021:
1. Gilbert Washington Wages (Form W-2) how many jobs did you have last year? 1
2. Tuition Statement Scholarship (Form 1098-T) and Gordon College Account Statement.
3. Tara Washington Retirement Income Annuities (Form 1099-R).
4. Tara Washington Social Security Retirement Benefits (Form SSA-1099).
5. Tara Washington Other income Gambling (Form W-2G) $3,000 Lottery $150.
6. Gilbert Washington Credit Card Debt Cancelled (Form 1099-C).
7. Gilbert and Tara Washington Canceled Check for refund direct deposit with Account Number and Routing Number.
Expenses and Documents – Year 2021:
1. College Tuition for a dependent (Form 1098-T) $5,218.
2. Gordon College Account Statement for Course – Related Books $450.
3. Supplies used as an educator, 1,280 hours in 2021 and $500 on unreimbursed classroom expenses.
4. Recovery rebate credit, claim Economic Impact Payment (EIP 3) $4,200 Line 30 Form 1040.
Advanced Scenario 7: Gilbert and Tara Washington Tax Return Preparation Step-by-Step (TaxSlayer VITA Training Software).
2021 1040 Personal Information:1. Filling Status: Married filing jointly
2. First Name Last Name Social Security Number (SSN)
3. Address
4. Dependents, Qualifying Child for Child Tax Credit, and Credit for Other Dependents
2021 1040 Income and Adjustments:
Line 1 (1040) Wages, salaries, tips. Attach Form W-2:
$35,502
Reference: 2021 IRS Publication 525 Taxable and Nontaxable Income For use in preparing 2021 Returns.
2021 What's New: Temporary Allowance of 100% Business Meal Deduction.
Line 5b (1040) Pensions and annuities Taxable amount:
18,035 Simplified Method Worksheet
Line 6b (1040) Social security benefits Taxable amount:
17,937 Social Security Benefits Worksheet
Line 8 (1040) Other income from Schedule 1, line 10:
$3,900
Line 9 (1040) Add lines 1 thru 8. This is your total income:
$75,37
Line 10 (1040) Adjustments to income from Sch1, line 26:
$250
Line 11 (1040) Your adjusted gross income (Line 10 minus Line 9):
$75,124
Line 12a (1040) Standard deduction:
$26,450
Line 15 (1040) Taxable income (Line 11 minus Line 12a):
$48,674
Line 16 (1040) Tax:
$5,443
Advanced Scenario 7: Test Questions Gilbert and Tara Washington (TaxSlayer VITA Training Software)
15. What is the taxable portion of Tara’s pension from Oak Enterprises using the simplified method?a. $0 b. $17,862 c. $18,035 d. $18,485
The first step in figuring how much of a distribution is taxable is to determine the cost of your pension or annuity, Publication 575 Pension and Annuity Income – IRS, Cost (Investment in the Contract).
Using Worksheet A. Simplified Method Worksheet for Tara Washington.
16. None of Tara’s social security income is taxable.
a. True b. False
6a Social security benefits 21102 and 6b Taxable amount 17937
17. What is the total amount of other income reported on the Washington’s Form 1040, Schedule 1?
a. $3,900 b. $3,150 c. $2,400 d. $750 Cancellation of Credit Card Debt
Tara won $3,000 gambling at a casino and had additional lottery winnings of $150. And plus $750 Cancellation of Credit Card Debt equals to $3,900.
Gambling Winnings and Losses:
The taxpayer may receive one or more Forms W-2G reporting gambling winnings. Total gambling winnings must be reported as Other income. If the taxpayer also had gambling losses, the losses can only be deducted on Schedule A.
Cancellation of Credit Card Debt, Form 1099-C:
Lenders or creditors are required to issue Form 1099-C if they cancel a debt owed to them of $600 or more. Generally, an individual taxpayer must include all canceled amounts (even if less than $600) on the Other income line of Form 1040, Schedule 1.
18. Gilbert is eligible to deduct $500 as an adjustment to income on Form 1040, Schedule 1 for qualified educator expenses.
a. True b. False
Deducting Teachers' Educational Expenses – IRS:
Eligible educators can deduct up to $250 of qualified expenses paid during the tax year. If the taxpayer and spouse are both eligible educators, they can deduct up to $500, but neither can deduct more than their own expenses up to $250.
19. The Washington’s standard deduction on their 2021 tax return is $________. 26450
The standard deduction for married filing jointly for tax year 2021 rises to $25,100. IF your filing status is Married filing jointly, AND the number of boxes checked is 1 for Was born before January 2, 1957, THEN your standard deduction is $26,450 per Form 1040 2021 Standard Deduction Chart.
20. The total qualified expenses for the American Opportunity Credit are $ _________. 3655
+$5,218 Tuition – Fall Semester 2021 +$450 Course Related Books -$2,013 Scholarship = $3655
21. Which of the following credits are the Washingtons’ eligible to claim on their tax return?
a. Child tax credit b. Credit for other dependents c. Child and dependent care credit d. None of the above
Child Tax Credit and Credit for Other Dependents:
The child tax credit is unique because if a taxpayer cannot benefit from the nonrefundable credit, the taxpayer may be able to qualify for the refundable additional child tax credit on Schedule 8812, Credits for Qualifying Children and Other Dependents. Understanding of this credit may result in lower tax for you.
What is credit for other dependents?
There is a $500 credit for other dependents who do not qualify for the $2,000 child tax credit. The dependent must be a U.S citizen, U.S. national, or resident of the U.S. The dependent must have a valid identification number (ATIN, ITIN, or SSN).
22. What is the Washington’s total federal income tax withholding? $________. 6669
Advanced Scenario 8: Test Questions Cynthia Simon (Tax return using TaxSlayer Training Software)
23. What is the net short term capital gain reported on Cynthia’s Schedule D?a. $2,350 b. $1,400 c. $650 d. $300
24. Which of the following cannot be claimed as a business expense on Cynthia’s Schedule C?
a. Cleaning supplies b. Business cards
c. Lunches d. Work gloves
Schedule C Part II: Expenses:
On Schedule C there are separate lines for the most common expenses that are incurred in a business. Lunches are not ordinary and necessary expense for that business.
25. What is the amount Cynthia can take as a student loan interest deduction on her Form 1040, Schedule 1? $__________________. 2500
26. What is the total amount of advanced premium tax credit that Cynthia received in 2021?
a. $3,960 b. $2,400 c. $1,800 d. $150
27. What is the amount of Cynthia’s lifetime learning credit? $_______________. 400
Qualifications to claim the Lifetime Learning Credit:
• Lifetime learning credit can be claimed for an unlimited number of years.
• Lifetime learning credit is a non-refundable credit of up to $2,000.
• The law requires that the student must generally receive a Form 1098-T, Tuition Statement, in order for the taxpayers to claim the education credit. Amounts paid must be paid to the educational institution.
28. Cynthia will have to pay $200 additional tax because she received the early distribution from her IRA.
a. True b. False
Exceptions to Tax on Early Distributions:
A taxpayer who has taken an early distribution from an IRA may take an exception to the 10% additional tax if the taxable part of the distribution is less than or equal to the adjusted qualified education expenses. Attach Form 5329 TAX ON EARLY RETIREMENT DISTRIBUTION.
29. How can Cynthia prevent having a balance due next year?
a. She can increase the withholding on her Form W-4
b. She can make estimated tax payments
c. She can use the IRS withholding calculator to estimate her withholding for next year.
d. All of the above
1. If taxpayer needs to adjust the amount withheld, taxpayer may submit a revised Form W-4.
2. Taxpayer can make estimated tax payments.
3. Taxpayer to use the Tax Withholding Estimator to check withholding for next year.
Advanced Scenario 9: Richard Cook Interview Notes (Tax return using TaxSlayer Training Software).
• Richard is age 39 and was widowed in 2017.He has a daughter, Isabella, age 5.• Richard provided the entire cost of maintaining the household and over half of the support for Isabella. In order to work, he pays childcare expenses to Busy Bee Daycare.
• Richard declined to receive advance child tax credit payments in 2021.
• Richard’s earned income in 2019 was $19,000.
• Richard and Isabella are U.S. citizens and lived in the United States all year in 2021.
• Richard received the third Economic Impact Payment (EIP3) in the amount of $2,800 in 2021.
Advanced Scenario 9: Richard Cook Test Questions.
30. What is Richard’s most advantageous filing status?a. Single b. Married Filing Separately
c. Head of Household d. Qualifying Widower
A widow or widower with one or more qualifying children may be able to use the Qualifying Widow(er) filing status, which is available for two years following the year of the spouse’s death. Richard’s most advantage filing status is Qualifying Widower but he was widowed in 2017 and this is more than 2 years. Therefore he must use Head of Household filing status.
31. Richard’s adjusted gross income on his Form 1040 is $__________? 41580 How is taxpayer’s Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) used?
The taxpayer’s total Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is the amount that is used to compute some limitations, such as the medical and dental deduction on Schedule A and the credit for child and dependent care expenses.
How is taxpayer’s Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) calculated:
1. Add the Income section. This is the taxpayer’s total income.
2. Add the Adjustments to Income section. These are the total Adjustments.
3. Subtract the Schedule 1 adjustments from the total income. This is the AGI.
32. Richard can claim the following credits on his tax return.
a. Child Tax Credit b. Child and Dependent Care Credit
c. Both a and b d. Neither a nor b
33. Richard’s Retirement Savings Contributions Credit on Form 8880 is $_______. 100
How you handle IRA contributions?
1. Taxpayers may be able to deduct some or all of their contributions to the IRA.
2. Amounts in an IRA, including earnings, are not taxed until distributed.
3. Contributions may be eligible for the retirement savings contributions credit.
34. Richard will use his 2019 earned income rather than his 2021 earned income to calculate the earned income tax credit on his 2021 tax return because his 2019 earned income is higher than his 2021 earned income.
a. True b. False
Richard’s 2019 earned income is $19,000, and Richard’s 2021 earned income is $41,500.
1040 Tax Form Changes for 2021:
Line 27c is added for taxpayers to include their 2019 earned income if they elect to use that amount when figuring their earned income credit.
35. Richard’s child and dependent care credit from Form 2441 is reported as a nonrefundable credit on Form 1040, Schedule 3.
a. True b. False
Credit for child and dependent care expenses from Form 2441, line 11 is reported on Form 1040, Schedule 3, Line 2, Attach Form 2441.
Where can you find answers to additional questions about the CTC? For up to date information about the CTC and reconciling advance payments, go to https://www.irs.gov/credits-deductions/advance-child-tax-credit-payments-in-2021.
2021 International Course Scenarios and Test Questions:
2021 International Exam Certification 93% Pass Proof.Directions:
The first two scenarios do not require you to prepare a tax return. Read the interview notes for each scenario carefully and use your training and resource materials to answer the questions after the scenarios. The answers are in bold.
International Scenario 1: Andy and June Hillsdale — Interview Notes;
• Andy and June currently live in Hong Kong.• They moved there on February 15, 2020 and rent a 2-bedroom apartment. Andy was transferred there for an indefinite period of time. Andy and June intend to eventually return to the United States.
• Andy is employed by a U.S.-based Fortune 500 company and June teaches English as a second language.
• Andy and June returned to the U.S. for 7 days for a family funeral in August of 2021.They also took a 13 day vacation to Macao, China to gamble and relax.
• Neither Andy nor June work for the U.S. government.
• Andy and June have a house in the U.S. It is vacant while they are overseas. Their brother and sister-in-law house sit while they are living abroad.
• Andy and June are U.S. citizens and have valid Social Security numbers.
International Scenario 1: Andy and June Hillsdale — Test Questions and Answers;
1. When calculating the 330 full days in a foreign country for the physical presence test, how is the 13-day vacation treated?a. None of days are counted as days spent in a foreign country
b. Only the first and last days of the trip do not count as days spent in the foreign country
c. All of the days are counted as days spent in the foreign country
d. Only 5 of the 13 days count as spent in the foreign country
2. In order for Andy and June to exclude their foreign earned income, they must ________.
a. Have income that qualifies as foreign earned income
b. Demonstrate that their tax home is in a foreign country
c. Meet the physical presence test
d. All of the above
Question 1 — Explanation:
What is the difference between physical presence test and bona fide residence test?
IRS physical presence test definition:
You meet the physical presence test if you are physically present in a foreign country or countries 330 full days during any period of 12 consecutive months.
Determination that you meat tax home test in a foreign country is explained under Chapter 4 of Publication 54, Tax Guide for U.S. Citizens and Resident Aliens Abroad.
IRS Bona fide residence test definition:
To qualify for bona fide residence, you must reside in a foreign country for an uninterrupted period that includes an entire tax year.
During the period of bona fide residence in a foreign country, you can leave the country for brief or temporary trips back to the United States or elsewhere for vacation or business.
The bona fide residence test applies to U.S. citizens and to any U.S. resident alien who is a citizen or national of a country with which the United States has an income tax treaty in effect.
If you go there to work for an indefinite or extended period and you set up permanent quarters there for yourself and your family, you probably have established a bona fide residence in a foreign country, even though you intend to return eventually to the United States.
Question 2 — Explanation:
What are the eligibility requirements to exclude foreign earned income?
To claim the foreign earned income exclusion, taxpayers must:
International Scenario 2: Wilhelm and Mary Schmidt — Interview Notes;
• Wilhelm and Mary are married and live in Stuttgart, Germany.• Mary is a U.S. citizen and has a valid Social Security number. Wilhelm is a citizen of Germany and has an ITIN for U.S. tax filing purposes.
• In 2017, Wilhelm and Mary chose to treat Wilhelm as a resident alien for tax purposes. This choice has never been suspended or revoked.
• Wilhelm and Mary have a daughter, Helga, who was born on July 23, 2020.Helga is a U.S. citizen and has a valid Social Security number issued by the due date of the return, including extensions.
• When both of Wilhelm’s parents died last year, his uncle Hans moved in with them. Hans is a citizen of Germany and has no income.
• Mary is employed by a Fortune 500 company and earned $27,500.
• Wilhelm works as a part-time brewer and earned the equivalent of $18,000 in U.S. dollars.
• Wilhelm and Mary provide all the financial support for Helga and Hans.
International Scenario 2: Wilhelm and Mary Schmidt — Test Questions with Answers;
3. Neither spouse wishes to revoke their election to treat Wilhelm as a resident alien. What are Wilhelm and Mary’s filing status options this year?a. They must file Married Filing Separately
b. They must file Married Filing Jointly
c. Mary can chose to file Single and Wilhelm does not have to file at all
d. They can chose Married Filing Jointly or Married Filing Separately
4. How can the Schmidts decide to end their election to treat Wilhelm as a resident alien?
a. Divorce or Legal Separation
b. Revocation in writing
c. Death of either spouse
d. All of the above
5. On a Married Filing Jointly return, can Wilhelm and Mary claim the Credit for Other Dependents for Uncle Hans?
a. No, because Hans is not a U.S. citizen, U.S. national, U.S. resident alien, or a resident of Canada or Mexico
b. Yes, because Hans is a qualifying relative with no income
c. Yes, because Hans meets the relationship test d. None of the above
6. On a Married Filing Jointly return, Wilhelm and Mary are able to claim which of the following credits for Helga?
a. Child tax credit
b. Earned income credit
c. Other Dependents Credit
d. None of the above
Question 6 — Explanation: What is the amount of the Child Tax Credit for 2021? (Updated January 11, 2022)
For tax year 2021, the Child Tax Credit increased from $2,000 per qualifying child to:
• $3,600 for children ages 5 and under at the end of 2021 and
• $3,000 for children ages 6 through 17 at the end of 2021.
References:
1. 2021 IRS Fact Sheet updates the 2021 Child Tax Credit and Advance Child Tax Credit frequently asked questions (FAQs).
2. IRS 2021 Publication IRS User Guide: 5549, Child Tax Credit Update.
3. IRS 2021 Publication 5534-E, Advance Payments of the Child Tax Credit Which Online Tool Should I Use?.
If your situation has changed in 2021, updating this information, using Publication 5534-E, will help you get the most accurate amount of advance payments.
2021 IRS Publication 5549, user guide includes information to help you how to use the IRS’s Child Tax Credit Update Portal to:
• Check if you’re enrolled to receive advance payments.
• Un-enroll from advance payments of the Child Tax Credit.
• Update or provide bank account information for direct deposit.
• View the status of your payments.
• Update or provide a mailing address.
Additional Information:
1. 2021 Publ. 501 Dependents, Standard Deduction, and Filing Information, for use in preparing 2021 RETURNS.
2. 2021 Publ. 596 Earned Income Credit (EIC), for use in preparing 2021 RETURNS.
International Scenario 3: Justin Herzing — Interview Notes;
• Justin Herzing is a U.S. citizen, single, and has no children. He has lived and worked in England since March 20, 2013.He does not maintain an address in the U.S. and has no intentions of returning.• He considers himself a resident of England. He rents an apartment at 700 Bond Street, London, UK W2SC5.
• Income:
— Justin’s visa type: Unlimited.
— Justin works at the U.S. Embassy and has a Form W-2 for his salary.
— In 2021, Justin got a job working part time in a pub as a waiter. The pub is called the Tilted Crown and located at 256 Oxford Street, London, UK, 2WSC4.Justin earned an equivalent of $4,790 in wages and paid taxes totaling $295. His taxes were paid to England as he earned his wages.
— Justin earned $215 (converted to U.S. dollars) of dividends from Rothchilds Corp. He paid foreign tax to England on these dividends in the amount of 33.0 Pounds. The exchange rate on the date he paid the tax was 1 U.S. Dollar (USD) = 0.746 Pounds. Justin’s dividends are not qualified dividends for U.S. tax purposes.
• Justin was not required to file FinCen Form 114 and he did not receive a distribution, was not a grantor of, nor was he a transferor to a foreign trust.
• Justin did not itemize in 2020 and does not have enough deductions to itemize in 2021.
• Justin received a $1,400 Economic Impact Payment (EIP 3) in March 2021.
International Scenario 3: Justin Herzing — Test Questions with Answers;
7. What is the maximum amount of foreign earned income excluded from Justin’s tax return?a. $0 b. $4,790 c. $46,530 d. $51,320
Question 7 — Explanation: Justin earned an equivalent of $4,790 in wages and paid taxes totaling $295. His taxes were paid to England as he earned his wages.
The foreign tax credit is different from the foreign earned income exclusion. If the taxpayer uses the foreign earned income exclusion, foreign tax paid on the excluded income cannot be used to claim the foreign tax credit.
8. Justin does not have to report his dividend income from Rothchilds Corp. because:
a. Form 1099-DIV was not issued to him
b. He already paid foreign taxes to England on his dividends
c. Foreign passive income is not taxable
d. None of the above. He must report his worldwide income, which includes his dividend income.
Question 8 — Explanation: Justin’s dividends are not qualified dividends for U.S. tax purposes. There are two types of ordinary dividends: qualified and nonqualified. The difference between the two is that nonqualified dividends are taxed at ordinary income tax rates. For a definition of qualified dividends, refer to Publication 550, Investment Income and Expenses.
9. General category income consists of income earned in a foreign country that an individual does not exclude, or excludes only part of, under the foreign earned income exclusion.
a. True b. False
Question 9 — Explanation:
• Justin is a U.S. citizen who lives and works in England. Justin earned $215 (converted to U.S. dollars) of dividends from Rothchilds Corporation.
• Justin paid foreign tax to England on $215 dividends in the amount of 33.0 Pounds. The exchange rate on the date he paid the tax was 1 U.S. Dollar (USD) = 0.746 Pounds. Therefore 33 Pounds divided by 0.746 Dollar = 44 U.S. Dollars.
• Justin paid foreign tax in the amount of $44 to England on his $215 dividends income. and $44 divided by $215 = 20% income tax rate.
• Justin Herzing is a U.S. citizen who lives in England and in 2021 he paid 20% income tax rate on $215 dividends income from Rothchilds Corporation.
• For the tax purpose of Form 1116, Justin’s foreign dividend income should be classified as Passive Category Income or General Category Income. Dividends Income Tax qualifies for the foreign tax credit and qualifies as a Passive Category Income, because it is less than 37% of the highest U.S. income tax rate. Reference: IRS Publication 514, Foreign Tax Credit for Individuals for preparing 2021 RETURNS.
• Since 20% tax rate, Justin paid on dividend income is no more than the highest 37% U.S. income tax rate, Justin’s income falls under the “Passive Category Income”.
IRS, what is the highest U.S. income tax rate 2021:
For tax year 2021, the top tax rate remains 37% for individual single taxpayers with incomes greater than $523,600.
10. Which source of Justin’s income qualifies for the foreign earned income exclusion?
a. Wages from the pub
b. Dividends from Rothchilds Corp
c. Wages from U.S. Embassy
d. None of the above
Question 10 — Explanation:
• General category income consists of income earned in a foreign country that an individual does not exclude, or excludes only part of, under the foreign earned income exclusion.
• What type of income qualifies for foreign earned income exclusion? You may qualify to exclude your foreign earnings from income up to an amount that is adjusted annually for inflation $108,700 for 2021, and $112,000 for 2022. In addition, you can exclude or deduct certain foreign housing amounts.
• Foreign Earned Income Exclusion; If you meet certain requirements, you may qualify for the foreign earned income exclusion. To claim the foreign earned income exclusion, you must have foreign earned income, your tax home must be in a foreign country and you must be a U.S. citizen or a U.S. resident alien who is physically present in a foreign country or countries for at least 330 full days during any period of 12 consecutive months.
11. Justin does meet the requirements of the bona fide residence test and can exclude his foreign earned income.
a. True b. False
Question 11 — Explanation: To claim the foreign earned income exclusion, taxpayer must;
• Demonstrate that their tax home is in a foreign country.
• Meet either the bona fide residence test or the physical presence test.
• Have income that qualifies as foreign earned income.
12. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Justin has both passive and general categories of foreign income
b. Justin can take the foreign tax credit for the income taxes paid on his dividend income from Rothchilds Corp and has to file the Form 1116, Foreign Tax Credit
c. Justin can claim both the foreign tax credit for the $295 income taxes paid to England and exclude the $4,790 foreign earned income from his part time job at the pub
d. Justin can claim the foreign earned income exclusion of $4,790 from his part time job at the pub. Therefore, he cannot take the foreign tax credit for the $295 income taxes paid to England
Question 12 — Explanation: Can you take a foreign tax credit for taxes on income you excluded or could have excluded? Once you choose to exclude foreign earned income and/or foreign housing costs, you cannot take a foreign tax credit for taxes on income you excluded or could have excluded.
13. Justin must include the amount of foreign tax paid to England as withheld Federal income taxes. a. True (b. False)
Question 13 — Explanation: How do I claim foreign tax withheld?
File Form 1116, Foreign Tax Credit, to claim the Foreign Tax Credit (FTC) and File Form 2555, Foreign Earned Income to claim the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE), which allows those who qualify to exclude some or all of their foreign-earned income from their U.S. taxes. Corporations file Form 1118, Foreign Tax Credit—Corporations, to claim a foreign tax credit.
14. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Once the election is made to exclude foreign earned income, that choice remains in effect for that year and all later years until revoked
b. The foreign earned income exclusion is voluntary
c. The election for the foreign earned income exclusion is made by completing the Form 2555, Foreign Earned Income
(d. All of the above.)
Question 14 — Explanation: Once you choose to exclude your foreign earned income, filing Form 2555, that choice remains in effect for that year and all later years unless you revoke it. 15. What is the amount of foreign taxes paid on the dividend income, converted to U.S. dollars? (Round to the nearest dollar).
a. $25 b. $44 c. $187 d. $335
Question 15 — Explanation:
1 U.S, Dollar = 0.746 Pounds and therefore 33 Pounds Divided by 0.746 = $44 U.S. Dollars and the correct answer.
2021 Military Course Scenarios and Test Questions with Answers and Explanations:
2021 Military Exam Certification 93% Pass Proof.
Directions:For Interview Notes refer to 2021 Publication 6744 VITA/TCE Volunteer Assistor’s Test/Retest. The first four scenarios do not require you to prepare a tax return.
Military Scenario 1: Todd Long — Test Questions.
1. Todd is not able to take an adjustment to income for:a. Travel to and from duty station
b. Meals
c. Both a and b
d. Uniforms
2. What is the amount of the deductible mileage expense? $______________. 2016 = 3,600 miles X $0.56
Question 1 — Explanation: The cost and upkeep of reservist’s uniforms, suitable to wear off duty, is not allowable as an adjustment to income.
Question 2 — Explanation:
What is the IRS issued Standard Military Mileage Rate for 2021?
Military Privately Owned Vehicle (POV) Mileage Reimbursement Rates for Year 2021 is 56 cents per mile driven for business use, 16 cents per mile driven for medical or moving purposes for qualified active duty members of the Armed Forces.
Todd’s duty station is 150 miles away from his residence. He drove 3,600 miles to and from his duty station based on his travel log.
What is the 100-mile rule for reservists?
Military reservists who must travel more than 100 miles away from home to attend a drill are able to deduct their travel expenses as an adjustment to income.
Military Scenario 2: Dave and Sandra Blackburn — Test Questions.
3. Their net financial profit from the move will be reported on:a. Form 1099-INT, Interest Income
b. Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement
c. Form 1040 Schedule A, Itemized Deductions
d. None of the above. It doesn’t need to be reported.
Question 3 — Explanation:
When the move is completed, the Armed Forces member provides receipts and paperwork to substantiate authorized expenses. The net financial profit is taxable and is reported on a separate Form W-2.
4. The Blackburns can deduct the cost of their side trip and house hunting trip as qualified moving expenses.
a. True (b. False)
5. How much can Dave and Sandra claim for the mileage $ _______. (Round to near¬est dollar).
a. $346 2,163 milesX$0.16 per mile for moving=$346
b. $380
c. $1,211
d. $1,332
Question 5 — Explanation:
In 2021, the standard IRS mileage rate is 56 cents per mile for business miles driven, 16 cents per mile for moving or medical purposes and 14 cents per mile for charity miles driven.
The Blackburns drove their rental truck a total of 2,378 miles. The shortest, most direct route calculated by the Navy was 2,163 miles.
6. How much can Dave and Sandra claim as their total qualified lodging expenses?
a. $0
b. $79
c. $316 $79 X 4 nights = $316
d. $362
Question 6 — Explanation:
The allow¬able lodging per diem was $79 per night. Dave and Sandra Blackburn’s trip took a total of nine days and eight nights instead of the authorized 4 nights for travel.
Military Scenario 3: Lisa Wagner — Test Questions.
7. Which of the following documents are issued by the VA for disability payments?a. Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement
b. Forms W-2 or 1099-R, depending on type of disability.
c. No tax form is required to be issued; however, Lisa may receive a statement.
d. Form 1099-R, Distributions From Pensions, Annuities, Retirement or Profit Sharing Plans, Insurance Contracts, etc.
8. The disability payment of $2,950 that Lisa received from the VA is non-taxable.
a. True b. False
Question 8 — Explanation: Disability benefits received from the VA should not be included in your gross income.
Military Scenario 4: Robert and Shirley Myers — Interview Notes.
• Robert and Shirley Myers are married and have a 13 year old daughter who lived with Shirley all year.• Robert was deployed to Afghanistan on June 1, 2021.His last day in the combat zone is scheduled for May 3, 2022.
• Robert’s Form W-2 shows:
Box 1 = $15,000
Box 12a = $20,000, Code Q
• Shirley’s Form W-2 shows $34,000 in Box 1. This is her only income.
• Robert, Shirley, and their daughter are all U.S. citizens and have valid Social Security numbers. The entire family lives in the U.S.
Military Scenario 4: Robert and Shirley Myers — Test Questions.
9. Robert and Shirley cannot choose to exclude their combat pay for the purposes of calculating the earned income credit. a. True b. FalseQuestion 9 — Explanation:
Nontaxable Combat Pay Election and the Earned Income Tax Credit;
If the family does not use the NCPE, then they would claim an EITC of $4,000. However, if the family were to include their nontaxable combat pay, then their EITC earned income increases to $20,000 and their EITC would increase by over $1,000 from $4,000 to $5,028.
By default, nontaxable combat pay is excluded from earned income. Nontaxable combat pay is listed on Form W-2, box 12, with Code Q.
Even though your nontaxable combat zone pay is excluded from income, you can elect to include your nontaxable combat zone pay in earned income for the purpose of calculating your Earn Income Credit (EIC). If you make that election, you must include in earned income all nontaxable combat zone pay you received.
10. Robert and Shirley have ______ days to file their 2021 tax return after he returns from the combat zone.
a. 105 b. 180 c. 288 d. 365
Question 10 — Explanation:
How long Robert has to file his tax return after he returns from the combat zone deployment?:
180 days.
Robert was deployed in the combat zone from June 1, 2021 through May 3, 2022. The deadline for filing Robert’s 2021 return is figured as follows:
The deadline for filing Robert’s income tax return is 180 days after his last day in the combat zone.
In addition to the 180 days extension, the extension includes the 108 additional days left in the filing period when Robert entered the combat zone.
The official deadline for filing 2021 federal income tax returns is April 18, 2022.
The 108 additional days are the number of days in the 3-1/2 month filing period that were left when Robert entered the combat zone (January 1 – April 18, 2021). Therefore the correct answer is 180 + 108 = 288 days.
May 3, 2022 is Robert’s last day of deployment in the combat zone. And therefore when adding 288 days to Robert’s last day of deployment, the deadline for filing Robert’s 2021 tax return is February 9, 2023.
How should the IRS be notified about combat zone service?
The IRS works with the Department of Defense to identify taxpayers who are serving in a combat zone. This may allow the IRS to suspend compliance actions, such as audits or enforced collections, until 180 days after the taxpayer has left the zone.
Military Scenario 5: Daniel and Betty Simmons — Test Questions
11. Daniel and Betty can claim $14,482 as their total rental expenses on their joint return?a. True b. False
Question 11 — Explanation: If you receive rental income from the rental of a dwelling unit, there are certain rental expenses you may deduct on your tax return. These expenses may include mortgage interest, property tax, operating expenses, depreciation, and repairs.
— Insurance: $1,900
— Management fees: $1,045
— Betty paid $1,373 to fix a broken window. Betty filled a pothole in the driveway, and repaired a broken pipe. The repair was worth $675 compared to the estimate from the asphalt contractor. The $675 Betty’s labor is not an eligible rental expense deduction but cost for imporvement. Betty may not deduct the cost of improvements. The cost of improvements is recovered through depreciation.
— Real estate property tax: $2,114.
— Mortgage Interest: $4,750.
— Depreciation: $3,300 (annual amount previously calculated by Betty’s accountant).
12. Code “Q” in box 12a of Daniel’s W-2 represents combat pay. a. True b. False
13. Which schedule is used to report rental income and expenses? a. Schedule F, Profit or Loss From Farming b. Schedule E, Supplemental Income and Loss c. Schedule D, Capital Gains and Losses d. Schedule C, Profit or Loss From Business
14. Combat pay ______________________
a. May increase the Earned Income Credit
b. May increase the Child Tax Credit
c. Is reported on Form W-2 in Box 12 with Code Q
d. All of the above
Question 14 — Explanation:
Though your combat zone pay is excluded from income, you can elect to include it in income in figuring your EIC.
15. Which of the following credits can be claimed for their son, Brian?
a. Credit for Other Dependents
b. Earned Income Credit
c. Child Tax Credit
d. Both a and b
Question 15 — Explanation:
IRS 18 year old child qualifies for Earned Income Credit and Credit for Other Dependents if under age 19 at the end of the year and younger than you (or your spouse, if you file a joint return).
2021 Foreign Student Exam with Answers and Explanations:
2021 Foreign Student Exam Certification 82% Pass Proof.Part 1 VITA/TCE Foreign Student Exam Certification Covers:
Filing status: If both married taxpayers are nonresident aliens, they CANNOT file as Married Filing Jointly, they must file as Married Filing Separately. Nonresident aliens must use either the Single or the Married Filing Separately filing status.
Only residents of Canada, Mexico, S. Korea, and India may qualify for the Qualifying Widow(er) with Dependent Child(ren) status, if applicable.
As an exempt individual you must file Form 8843, Statement for Exempt Individuals with IRS to explain the basis of your claim that you can exclude days of presence in U.S. for purposes of the substantial presence test.
When and Where To File:
If you are filing a 2021 Form 1040-NR, attach Form 8843 to it. Mail your tax return by the due date (including extensions) to the address shown in your tax return instructions.
If you don’t have to file a 2021 tax return, mail Form 8843 to the Department of the Treasury, Internal Revenue Service Center, Austin, TX 73301-0215 by the due date.
If you had no US income and are only filing IRS Form 8843, the deadline is June 15, 2022.
2021 Part 1 Foreign Student Test – Residency Status, Form 8843, and Filing Status 1-17:
1.Ken entered the U.S.as a student on July 30, 2018 in F-1 immigration status. He had never been to the United States before and he did not change immigration status during 2021. For federal income tax purposes, Ken is a resident alien for 2021.a. True
b. False Ken is a nonresident alien for 2021.
2. Helen is a visiting professor at the local university. Helen was a graduate student from June 2017 to May 2019 in F-1 immigration status. She re-entered the United States as a teacher on December 20, 2020 in J-1 immigration status. For federal income tax purposes, Helen is a nonresident alien for 2021.
a. True
b. False Helen is a resident alien for 2021.
3. Yusuf served as a visiting scholar in F-1 immigration status from March 2017 through June 2020.In August of 2021, Yusuf returned to the United States as a professor. For federal income tax purposes, Yusuf is a resident alien for 2021.
a. True Yusuf is a resident alien for 2021.
b. False
4. Juan came to the United States in F-2 immigration status with his wife on July 15, 2017. He has not changed his immigration status. For federal income tax purposes, Juan is a resident alien for 2021.
a. True Juan is a resident alien for 2021.
b. False
5.Emily lived with her parents in F-2 immigration status in the United States from August 2010 to June 2012. She returned to the U.S.to attend college in F-1 immigration status on December 5, 2019. Emily needs to file Form 8843 for 2021.
a. True
b. False Emily does not need to file Form 8843 for 2021.
Question 5: Explanation - Who Must File Form 8843: Emily lived in U.S. 2010 - 2012 and 2019 - 2020, 5 years and therefore she is a resident alien for tax purposes in 2021.
6. Polina entered the United States on July 30, 2016 in J-1 student immigration status. On January 10, 2020, her husband Dmitry joined her in J-2 immigration status. Because Polina is a resident alien this year, Dmitry does not need to file Form 8843 for 2021. He is electing to file married filing jointly with her.a. True
b. False Dmitry need to file Form 8843 for 2021.
7. Polina and Dmitry from Question 6 had a son, Alexander, while here in the U.S. on December 5, 2020. A Form 8843 does not need to be filed for Alexander for 2021.
a. True F8843 does not need to be filed for Alexander for 2021.
b. False
8. Sophie and Yves have been in the U.S. as students in F-1 immigration status, since August 2018. Their 12-year-old son, Vincent, has been attending a boarding school in the U.S. since June 2015 in F-1 immigration status. Sophie, Yves, and Vincent all need to file Form 8843 for 2021.
a. True.
b. False Sophie, Yves, and Vincent don’t need to file F8843 2021.
9. Celeste is from Pakistan and is a Ph.D. student in communications engineering who is going to defend her dissertation in June. She arrived in the U.S. as a student on July 20, 2018. Celeste is a resident alien for tax purposes in 2021.
a. True
b. False Celeste is a nonresident alien for tax purposes in 2021.
10. Marcus is a junior majoring in biology. He is in the U.S.in F-1 immigration status from Germany. He transferred from a German university and arrived in the U.S. on December 30, 2018. Marcus worked in a lab on campus in an approved summer internship program for a company in New York. He will graduate in May, 2022. The company issued him a Form 1099-NEC. Marcus is considered a resident alien for tax purposes since the company issued him a Form 1099-NEC.
a. True
b. False Marcus is still considered a nonresident alien for tax purposes.
11. Nico is a nursing student from Greece who first arrived in F-1 immigration status on August 15, 2021. He does not have a tax identification number and he did not work or receive a scholarship in 2021, but had $75 interest income from his U.S. savings account his parents set up for him to pay for school and his living expenses. Nico must file Form 8843, and also Form 1040-NR to report his interest income for 2021.
a. True
b. False Nico must only file Form 8843.
12. Bo entered the U.S.in J-1 immigration status as a trainee in January 2019, and lives alone. His wife, Mei, could not accompany him because she had to care for her ailing parents. Bo can file as Single because he did not live with his spouse at all during 2021.
a. True
b. False Bo must file as Married Filing Separately.
13. Alex and Kim were married in March 2016, and the next year they both entered the U.S.in F-1 immigration status to complete their studies as Fulbright schol¬ars. Currently, Alex lives in San Diego, where he is completing his graduate work. However, Kim left him in March 2020 and has not been heard from since. Her parents will not tell him where she lives and he has not heard from her since. Since Alex does not know Kim’s whereabouts, he can file using the Single filing status.
a. True
b. False Alex must file using Married Filing Separately filing status.
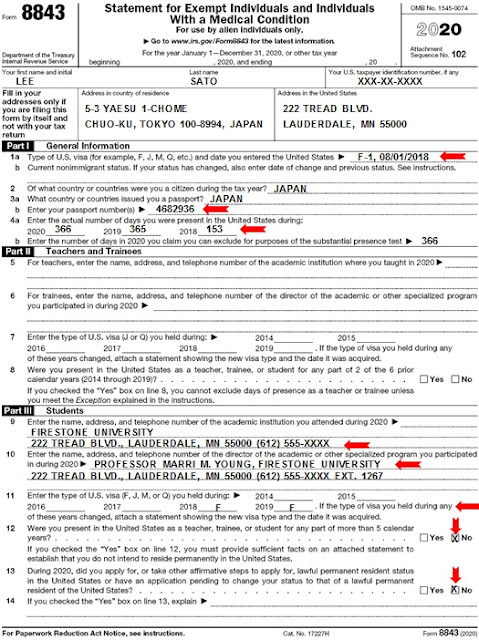
2020 Scenario 1: Lee Satō: 14-17 (4)
Use the following information to prepare Form 8843. (The correct answers are in parentheses.)• Lee Satō came to the U.S. to study on August 1, 2018, in F-1 immigration status. Her passport number is 4682936 and it was issued by her home country, Japan. Her home address is 5-3 Yaesu 1-Chome, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 100-8994, Japan. Her address at school is Firestone University, 222 Tread Blvd., Lauderdale, MN 55000. Her U.S. taxpayer identification number is XXX-XX-XXXX.
• Lee is attending Firestone University, 222 Tread Blvd., Lauderdale, MN 55000, tele¬phone 612-555-XXXX. Her specialized program is Alternative Fuel Systems and the director is Professor Marri M. Young, also at 222 Tread Blvd., Lauderdale, MN 55000, telephone 612-555-XXXX ext. 1267.
• Lee has not taken steps to apply for permanent residency. Lee had no income, so she is not required to file any other tax forms. Lee has not left the U.S. since arriv¬ing.
• After completing the required tax form, review the scenario and resource materials, and answer each of the test questions.
2021 Scenario 1: Enrique Satō Test Questions 14-17 (4).
Directions:
To answer the following multiple choice questions, refer to the Form 8843 you completed for Enrique Satō.
14. What should Enrique enter on Line 1b?
a. Leave blank
b. F1 January 1, 2020 H1b
c. F1
15. Enrique has to complete Lines 4a and 4b.
a. True
b. False
16. Enrique only has to complete Part 1 of Form 8843.
a. True
b. False)
17. What is the due date of Lee’s Form 8843 for tax year 2021?
a. April 18, 2022
b. June 15, 2022 Correct
c. October 15, 2022
d. December 31, 2022
Question 17 — Explanation: Deadline for submitting Form 8843 to IRS, even if you have had no income in 2021, you must file and submit the IRS Form 8843; the deadline to submit your Form 8843 is June 15, 2022. Dependents in F-2 and J-2 status must also file Form 8843.
2021 Form 8843 Statement for Exempt Individuals, Scenario 1, Enrique Satō, Peru, Sheet 1:
2021 Form 8843 Statement for Exempt Individuals, Scenario 1, Enrique Satō, Peru, Sheet 2:
Form 8843 can't be E-Filed. Mail Form 8843 by the due date June 15, 2022 to:
Department of the Treasury,
Internal Revenue Service,
Austin, TX 73301-0215
Exempt Individual - Who is a Student:
A student is any individual who is temporarily in U. S. on an "F, " "J, " "M, " or "Q " visa for the primary purpose of studying at an academic institution or vocational school, and who substantially complies with the requirements of that visa.
2021 Form 8843 Instructions:
Who must file:
You must file Form 8843 to claim days of presence in U. S. for purpose of the substantial presence test. To exclude days of presence as a student, complete Parts I and Part III of Form 8843. You must file even if you had no income in year 2021, by the deadline June 15, 2022.
Part I — General Information.
You are required to complete lines 1a through 4a and 4b of Form 8843 if you’re filing Form 8843 by itself and not filing Form 1040-NR.
Line 1a.
Type of U.S. visa (for example, F, J, M, Q, etc.) and date you entered the United States.
Line 2.
Of what country or countries were you a citizen during the tax year?
Line 3a.
What country or countries issued you a passport?
Line 3b.
Enter your passport number(s)
Line 4a.
Enter the actual number of days you were present in the United States during: 2020, 2019, 2018.
Line 4b.
Enter the number of days in 2020 you claim you can exclude for purposes of the substantial presence test.
Part III — Students:
If you qualify to exclude days of presence as a student, complete Part I and Part III of Form 8843 only.
Line 9. Enter the name, address, and telephone number of the academic institution you attended during 2020
Line 10.
Enter the name, address, and telephone number of the director of the academic or other specialized program you participated in during 2020.
Line 11.
Enter the type of U.S. visa (F, J, M, or Q) you held during: 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019. If the type of visa you held during any of these years changed, attach a statement showing the new visa type and the date it was acquired.
Line 12.
Were you present in the United States as a teacher, trainee, or student for any part of more than 5 calendar years? Yes or No.
If you checked the “Yes” box on line 12, you must provide sufficient facts on an attached statement to establish that you do not intend to reside permanently in the United States.
Line 13.
During 2020, did you apply for, or take other affirmative steps to apply for, lawful permanent resident status in U. S. or have an application pending to change your status to lawful permanent resident of U. S.? Yes or No.
Line 14.
If you checked the “Yes” box on line 13, explain.
2021 Part 2 Foreign Student Test – Taxability of Income, ITINs, and Credits 18-37:
Introduction: This segment of the VITA/TCE certification test includes 7 general and 12 scenario-based multiple choice questions on taxability of income, ITINs, and credits.18. Margarita, who is a nonresident alien and is in the United States in J-1 immigration status, spent $4,400 on qualifying tuition and educational expenses. She is entitled to claim an education credit on her tax return.
a. True b. False
Question 18 — Explanation:
Education Credits — If the taxpayer is a nonresident alien for any part of the year, they generally can’t claim the educational credits, such as the American Opportunity Credit and Lifetime Learning Credit.
19. Ji-yoo received $73 of dividend income on U.S. stocks she purchased online. She is an international student from Canada in F-1 immigration status. She arrived in the United States in 2020. Ji-yoo’s dividend income will be taxed at 30% on Form 1040-NR, Schedule NEC.
a. True b. False
Question 19 — Explanation: Tax Treaties/ Taxation Rate - Dividends (paid by U.S. Corporations).
Dividend Income: Generally, dividend income from investments in U.S. corporate stock is income, NOT effectively connected to the taxpayer’s U.S. trade or business and is therefore taxable at a 30% rate on Form 1040-NR, Schedule NEC.
20. Marie and Nathan are a married nonresident alien couple from France. Both are in the U.S. in F-1 immigration statuses and arrived in 2021. They paid $3,700 in childcare expenses, while attending school, for their child who was born in the United States and is a U.S. citizen. They are eligible to claim the child and dependent care credit on their Form 1040-NR.
a. True b. False
Question 20 — Explanation: Marie and Nathan are not eligible to claim the child and dependent care credit they can only claim the credit if they file a joint return.
21. Antero is a student in J-1 immigration status from Latvia. He earned $2,300 in wages in 2021. His wages are reported to him on Form 1042-S (Box 1, Income Code 20). Antero should report these wages on Form 1040-NR, Schedule OI.
a. Yes b. No
Question 21 — Explanation: If the income is exempt from tax by treaty, complete item L of Schedule OI (Form 1040-NR) and line 1c on page 1 of Form 1040-NR.
Schedule OI (Form 1040-NR).
For item L, identify the country, tax treaty article(s) under which you are applying for a refund of tax, the number of months in prior years that you claimed the treaty benefit and the amount of exempt income in the current year. Also attach Form 8833 if required.
22. Gus is a student here in J-1 immigration status as of October 15, 2021. Under the terms of his visa, he is permitted to work in the U.S. Gus does not qualify for a Social Security number and should apply for an ITIN.
a. True b. False
Question 22 — Explanation: Generally, students who enter the United States in an immigration status which allows them to be employed in the United States are eligible to apply for a Social Security Number (SSN) from the Social Security Administration. If a student is granted permission to work, Social Security and Medicare taxes are not withheld from their pay.
23. Elena, in F-1 student immigration status from Romania, is on the basketball team. She arrived in the U.S. on June 18, 2021 on a full athletic scholarship that includes payments for her room and board. The amount of her scholarship for room and board is taxable.
a. True b. False
Question 23 — Explanation: Countries with Treaty Benefits for Scholarship Grants (Income Code 16). Full Athletic Scholarship grants that cover room, board and other personal expenses are subject to U.S. tax unless a treaty benefit (as summarized below) exists.
24. Gunther is a student in the U.S. in F-1 immigration status. He arrived from Germany on July 13, 2019. Gunther worked in the bookstore and earned $2,500 in wages and had federal income tax withholding of $215. Gunther needs to file Form 1040-NR and Form 8843 for 2021.
a. True b. False
Scenario 2: Kim Lee Test Questions 25-29 (5).
Directions: To answer the following multiple choice questions, refer to the Form 1040-NR you completed for Kim Lee. Attach any Form 1042-S you received for treaty-exempt income.
25. What amount is entered on the line for wages, salaries, tips, etc. on Form 1040-NR?
a. $2,000
b. $6,000
c. $8,500 from Form W-2 Box 1
26. What is on the line for Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) on Form 1040-NR?
a. $0
b. $2,000
c. $6,000
d. $8,500
27. What is on the line for Itemized Deductions on Form 1040-NR?
a. $0
b. $80
c. $7,920
d. $8,000
28. What is the amount on the line for taxable income on Form 1040-NR?
a. $0
b. $1,920
c. $5,920
d. $8,420
29. Is $8,000 the total amount entered into Income Exempt from Treaty in Schedule OI?
a. Yes b. No
Scenario 3: Rudra Khatri Test Questions 30-33 (4).
Directions: To answer the following questions, refer to the Form 1040-NR you completed for Rudra Khatri.
30. What amount is entered for wages, salaries, tips, etc. on Form 1040-NR?
a. $25,200
b. $22,375
c. $22,350
d. $17,350
31. What amount is entered on the itemized deductions line on Form 1040-NR?
a. $13,785
b. $13,600
c. $12,550
d. $1,235
32. What is the amount of federal income tax withheld on Form 1040-NR?
a. $3,985
b. $3,900
c. $2,700
d. $1,050
33. What amount is on the taxable income line of the Form 1040-NR?
a. $21,300
b. $21,140
c. $9,825
d. $9,700
Scenario 4: Gergana Alferov Test Questions 34-37 (4).
Directions: To answer the following multiple choice questions, refer to the Form 1040-NR you completed for Gergana Alferov.
2021 Form W-2 Wage and Tax Statement for Gergana Alferov.
34. What amount is Gergana allowed as a treaty benefit?
a. $15,220
b. $9,000
c. $0
35. What is the amount entered on Form 1040-NR on the line for wages, salaries, tips, etc.?
a. $0
b. $6,220 This is the correct answer per IRS. IRS Error.
c. $9,000
d. $15,220 This should have been the Correct Answer. IRS Error.
36. Where on the tax return will Gergana enter her treaty benefits information?
a. Schedule OI, Line L then carried to Form 1040-NR, Line 1c
b. Form 1040-NR, Schedule A, Line 7
c. Treaty benefits are only subtracted from wages, salaries, tips, etc. and listed on Form 1040-NR, Line 1c.
d. No treaty amounts are allowed without Form 1042-S.
37. What is the amount of itemized deductions that Gergana is entitled to take? And what is her taxable income?
a. $622 and $10,244
b. $622 and $14,598
c. $220 and $6,000 This is the correct answer per IRS. IRS Error.
d. $220 and $15,000 This should have been the Correct Answer. IRS Error.
2021 Part 3 Foreign Student Test – Refunds, Deductions, and the Best Form to Use 38-50:
Introduction: This part of the VITA/TCE certification test includes 13 true/false or multiple choice ques¬tions. Foreign Students, Scholars, Teachers, Researchers and Exchange Visitors: Who Must File and Deductions.38. Emily, an international student from Ireland, has a Form W-2 that shows amounts withheld for Social Security and Medicare taxes. Emily is an F-1 student who arrived in 2018. What form should Emily use to claim a refund of her Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld?
a. Form 1040-NR
b. Form 8843
c. Form 843
39. Jose and Maria are from Mexico. Jose is a scholar at a local university in J-1 immigra¬tion status and Maria is in J-2 immigration status. Maria worked at a local boutique in 2021. Her Form W-2 shows Social Security and Medicare withholding. Maria found out her spouse does not have to pay Social Security or Medicare taxes. Maria is not eligible for a refund of her Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld.
a. True b. False
40. Li, an international student from People’s Republic of China, received $10,100 of interest income in 2021 from a personal bank account in the U.S. he opened when he first arrived on August 27, 2016. He also had a $100 capital gain from some U.S. stock he sold. What form and schedules does Li need to complete?
a. He does